Introduction to the Boeing 747
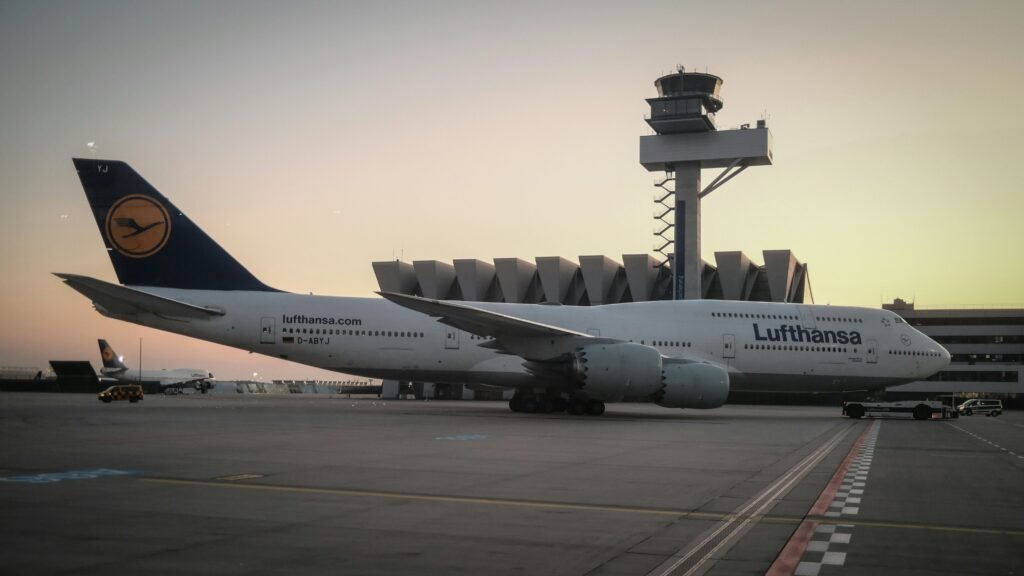
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” stands as a monumental achievement in the world of aviation, marking a transformative era in commercial air travel. Introduced in the late 1960s, this aircraft was the first wide-body airplane to enter service, which fundamentally redefined the standards for long-distance air transportation. The innovative design of the Boeing 747 allowed airlines to efficiently carry a significantly larger number of passengers and cargo, thereby expanding the possibilities of air travel and connecting economies worldwide.
The development of the Boeing 747 was spearheaded by Boeing in response to growing air travel demand and the need for a more efficient means of transporting passengers and freight. Its distinctive humpbacked appearance and immense size quickly made it an icon in the aviation industry. With the ability to accommodate hundreds of passengers, this aircraft broke barriers, making international travel more accessible and affordable. The 747 also introduced advanced technologies for its time, including high bypass ratio engines and sophisticated aerodynamics, contributing to its long-range capabilities.
<pthroughout 747=”” 747-400=”” 747-8=”” across=”” adapting=”” aircraft=”” airlines=”” and=”” as=”” aviation=”” boeing=”” but=”” comfort,=”” competitive=”” cutting-edge=”” efficiency,=”” emerge.=”” enhancements=”” ensure=”” even=”” evolving=”” found=”” fuel=”” globe.
The Evolution of the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” has a storied history that reflects the evolution of commercial aviation itself. The original model, the 747-100, took to the skies in 1969, marking a pivotal moment in air travel. With a seating capacity of approximately 366 passengers, it was designed for long-haul flights, offering unprecedented comfort and speed. The 747-100 set the foundation for subsequent models, experiencing various upgrades that would redefine aircraft capabilities.
The advancement from the 747-100 to later models is a testament to Boeing’s commitment to innovation. The introduction of the 747-200 in the early 1970s brought enhancements such as increased range and payload capacity. Notably, it featured upgraded engines that not only improved performance but also reduced fuel consumption, catering to the growing demands of airlines for more efficient operations. This model was the first to incorporate the iconic upper deck, which would become a signature feature of the 747 family.
In the 1980s, the Boeing 747-300 emerged, equipped with stretched fuselage design, allowing for up to 450 passengers. This model offered improved aerodynamics, contributing to enhanced fuel efficiency. Furthermore, the 747-400 introduced digital flight deck technology, wingtip extensions, and improved engines, pushing the boundaries of speed and range. The capacity to fly non-stop on long-distance routes made it a favorite among airlines worldwide.
The latest variant, the 747-8, was introduced in 2012, showcasing modern advancements in technology and design. Featuring a length of 76.3 meters, it is the longest commercial aircraft ever produced. The 747-8 also provides impressive fuel efficiency and enhanced passenger experience, making it suitable for both freighter and passenger configurations. Each evolution of the Boeing 747 embodies the progression of aviation technology, meeting diverse market needs while maintaining the original spirit of the Jumbo Jet.
Specifications of the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” is a wide-body commercial aircraft that has significantly influenced long-distance travel since its introduction in the early 1970s. This iconic aircraft comes in several variants, each with its unique specifications, catering to a diverse range of flight requirements. The most recognizable model, the Boeing 747-400, showcases dimensions that define its stature in aviation.
With a length of approximately 231 feet and 10 inches (70.6 meters) and a wingspan measuring 211 feet and 5 inches (64.4 meters), the 747-400 stands as a giant in the sky. Its height reaches 20 feet and 9 inches (6.3 meters) at the tail, allowing for a spacious upper deck that has become a hallmark of its design. In terms of weight, the maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) for this variant is around 875,000 pounds (396,893 kilograms), underscoring its capacity to handle significant passenger and cargo loads.
The performance metrics of the Boeing 747 are nothing short of impressive. Its cruising speed is approximately 560 miles per hour (900 kilometers per hour), which allows for efficient long-haul travel. The aircraft can cover a maximum range of about 8,000 nautical miles (14,800 kilometers), making it a preferred choice for intercontinental flights. The fuel capacity of the Boeing 747-400 is approximately 57,285 gallons (216,840 liters), further enabling it to fly long distances without the need for frequent refueling stops.
When comparing various models, such as the 747-8, which features a length of 242 feet and 4 inches (73.9 meters) and a wingspan that expands to 224 feet and 7 inches (68.4 meters), it becomes evident how Boeing has continuously enhanced the specifications over time. Each variant of the 747 adapts to evolving market needs, ensuring its status as a leading aircraft for decades.
Dimensions of the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” holds a significant place in aviation history, not only for its pioneering role in commercial flight but also for its impressive dimensions. The aircraft boasts a remarkable wingspan that varies across its various models, with the Boeing 747-8 featuring a wingspan of approximately 68.4 meters (224 feet 7 inches). This expansive wingspan enables the aircraft to maintain stability and efficiency during flight, accommodating its ability to transport large numbers of passengers and cargo across long distances.
The fuselage length of the Boeing 747 is equally noteworthy. The Boeing 747-8 model measures around 76.3 meters (250 feet 2 inches), which makes it one of the longest commercial aircraft in operation. This substantial length is a significant factor in its ability to hold a large number of passengers, often exceeding 400 in a typical three-class configuration. The interior space accommodates features such as lounges and spacious seating arrangements that enhance the overall travel experience for passengers.
Furthermore, the cabin height of the Boeing 747 adds to its spacious feel, offering an internal height that reaches approximately 2.54 meters (8 feet 4 inches). This height permits the installation of multiple cabin levels and innovative designs, which not only enrich passenger comfort but also accommodate various amenities, including sleeping quarters in premium configurations.
To contextualize the aircraft’s size, comparisons with other aircraft, such as the Airbus A380 and Boeing 777, reveal the Boeing 747’s bulkiness and stature in the aviation landscape. While the A380 has a slightly greater wingspan and overall capacity, the 747 remains an iconic symbol of air travel that continues to impress with its dimensions and capabilities.
Capacity: Passengers and Cargo
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” has cemented its legacy as a formidable aircraft in the aviation industry, particularly due to its impressive capacity for both passengers and cargo. The various models of the Boeing 747, including the 747-100, 747-400, and the newer 747-8, showcase different configurations that significantly influence their seating arrangements and freight options.
In passenger configuration, the Boeing 747 can typically accommodate between 400 to 600 passengers, depending on the specific model and the airline’s chosen layout. For instance, the 747-8 Intercontinental, which is the latest variant, boasts a maximum seating capacity of approximately 660 passengers in a high-density configuration. This allows airlines flexibility in tailoring their services for both economy and premium travel classes, as the larger cabin space lends itself well to spacious seating arrangements.
The cargo capacity of the Boeing 747 is equally remarkable, with the dedicated cargo version, the 747 Freighter (F), offering significant volume and weight capabilities. The 747-400F can transport up to 140 metric tonnes of cargo, while the 747-8F can carry around 140 metric tonnes as well, featuring a nose that opens for easy loading of oversized freight. Moreover, the two-deck design of certain models facilitates efficient loading and unloading processes, making it a preferred choice among freight carriers.
Airlines must consider these variations in capacity when operating the Boeing 747, as the aircraft’s ability to transport a substantial number of passengers alongside considerable freight can lead to enhanced profitability. The dual nature of the aircraft, catering to both passenger and cargo needs, underscores its versatility and enduring relevance in the competitive aviation market.
Performance Specifications
The Boeing 747, often recognized as the “Queen of the Skies,” exhibits impressive performance specifications that have made it a popular choice among airlines for long-haul travel. One of the key performance metrics is its takeoff distance, which varies depending on the model and weight at departure. Generally, the Boeing 747 requires approximately 8,000 to 10,000 feet of runway for a successful takeoff. Factors such as aircraft weight, altitude, and environmental conditions play a crucial role in determining the exact distance required.
Upon takeoff, the climb rate of the Boeing 747 is another commendable feature. The aircraft achieves a climb rate of around 2,000 feet per minute, allowing it to reach cruising altitudes efficiently. This capability ensures that it can swiftly ascend to altitudes where fuel efficiency is optimized, thus enhancing operational effectiveness.
When considering fuel efficiency, the Boeing 747 boasts competitive figures for its class. Depending on the variant, it can cover approximately 8 to 9 nautical miles per gallon of fuel on long-haul routes. This impressive fuel consumption translates to lower operational costs for airlines, making it an economically viable option for intercontinental travel. Fuel efficiency, combined with its substantial passenger capacity, allows airlines to maximize profitability on various routes.
In terms of cruise speed, the Boeing 747 operates at a typical cruise speed of around Mach 0.85, facilitating timely arrivals for flights of extensive durations. The cruising altitude often settles between 35,000 to 40,000 feet, where atmospheric conditions reduce drag and optimize fuel burn. Collectively, these performance specifications not only highlight the operational capabilities of the Boeing 747 but also exemplify its critical role in the aviation industry, supporting diverse airline strategies and enhancing global connectivity.
Technological Innovations in the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” has undergone significant technological advancements since its inception. These innovations have transformed it into a more efficient and passenger-friendly aircraft, responding to the evolving demands of modern aviation. One of the most notable updates has been the introduction of advanced avionics. Newer models are equipped with state-of-the-art navigation and communication systems that enhance safety and operational efficiency. These systems not only improve the pilot’s situational awareness but also streamline air traffic management, contributing to smoother flights.
Furthermore, the Boeing 747 has seen a substantial overhaul in its engine technology. The latest iterations are fitted with fuel-efficient engines that significantly reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. These engines, such as the GEnx-2B67, utilize advanced materials and design methodologies to optimize performance while adhering to stringent environmental regulations. This shift towards more sustainable aviation practices reflects Boeing’s commitment to mitigating the ecological impact of air travel.
In addition to performance improvements, the Boeing 747 has also enhanced passenger comfort in response to evolving consumer expectations. Updated cabin designs incorporate larger windows, improved lighting, and sophisticated climate control systems, all aimed at enhancing the in-flight experience. Features such as quieter cabins and improved seating arrangements cater to the needs of modern travelers, making long-haul flights more enjoyable.
This blend of technological advancements showcases Boeing’s proactive approach to addressing contemporary challenges in aviation, including environmental sustainability and passenger satisfaction. The evolution of the Boeing 747 embodies the continuous pursuit of innovation within the aerospace industry, ensuring that it remains a vital component of global air travel.
Notable Achievements and Milestones
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” has made significant contributions to the aviation industry since its introduction. One of its most notable achievements was the maiden flight on February 9, 1969, which marked a pivotal moment in commercial aviation. This aircraft was the first wide-body airplane produced, allowing airlines to transport larger numbers of passengers over long distances, thus revolutionizing air travel and making it more accessible to the general public.
The 747’s size, capacity, and range have allowed it to set numerous world records throughout its operational history. For instance, the Boeing 747 holds the record for the highest number of passengers carried in a single flight. It achieved this feat in 1991 when a 747-400, during a charter flight, accommodated 1,088 passengers. This record showcases the aircraft’s impressive capability to serve vast numbers of travelers, which has been vital for both commercial airlines and charter operations.
<pmoreover, 747=”” 747’s=”” a=”” additionally,=”” airline=”” airlines=”” airways,=”” american=”” among=”” and=”” around=”” as=”” became=”” been=”” boeing=”” but=”” by=”” cargo=”” carrier=”” choice=”” cornerstone=”” customer,=”” employed=”” enabled=”” expanding=”” favorite=”” fleets=”” freight=”” globe.=”” has=”” in=”” instrumental=”” international=”” it=”” its=”” launch=”” major=”” making=”” not=”” of=”” only=”” operators.
Throughout its history, the 747 has been involved in many historic flights and events. From its use as the Air Force One for U.S. presidents to facilitating humanitarian missions, the aircraft has transcended its role as a commercial airliner. Its contributions to the aviation sector, adorned with various milestones, have left a lasting legacy in air travel, making the Boeing 747 an iconic symbol of progress in aviation technology.
Conclusion: The Legacy of the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747, often referred to as the “Jumbo Jet,” has left an indelible mark on the aviation industry since its first flight in 1969. This iconic aircraft revolutionized air travel by introducing larger passenger capacities, enabling airlines to ferry thousands of travelers across long distances more efficiently. This shift not only made air travel more accessible but also drove down ticket prices, allowing a wider demographic of passengers to experience flight. Over the decades, the 747 has become synonymous with intercontinental travel, carrying over 4.5 billion passengers in its lifetime.
The specifications of the Boeing 747 contributed to its prominence. Its distinctive hump and wide fuselage allowed for a spacious cabin layout and significant cargo capacity. This versatility made it a preferred choice for both passenger and freight transport. Airlines that embraced the 747 model enjoyed increased operational efficiency, the ability to maximize revenue, and enhanced customer experience through amenities that were previously unattainable on narrower aircraft.
<pas 747=”” a=”” ability=”” adapt=”” advancements=”” aircraft=”” aircraft’s=”” an=”” and=”” as=”” aviation=”” be=”” being=”” boeing=”” by=”” cargo=”” changing=”” come.